Ticket based authentication
- The
TGT - Ticket Granting Ticketis the first ticket obtained on a Kerberos system. The TGT permits the client to obtain additional Kerberos tickets orTGS. - The
TGS - Ticket Granting Serviceis requested by users who want to use a service. These tickets allow services to verify the user’s identity.
user requests a TGT → authenticate to the domain controller by encrypting the current timestamp with their password hash.
once verified → it sends the user a TGT for future requests
Lets say user wants to connect to a service
request TGS to KDC(Key Distribution Centre) presenting the TGT→ TGS given to MSSQL server for authentication
- stateless authentication protocol
- Domain Controller has → Kerberos KDC distributes ticket
AD - Kerberos
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), Domain Controllers have a Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) that issues tickets.
When a user initiates a login request to a system, the client they are using to authenticate requests a ticket from the KDC, encrypting the request with the user’s password. If the KDC can decrypt the request (AS-REQ) using their password, it will create a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) and transmit it to the user.
The user then presents its TGT to a Domain Controller to request a Ticket Granting Service (TGS) ticket, encrypted with the associated service’s NTLM password hash.
Finally, the client requests access to the required service by presenting the TGS to the application or service, which decrypts it with its password hash.
Kerberos Authentication Process
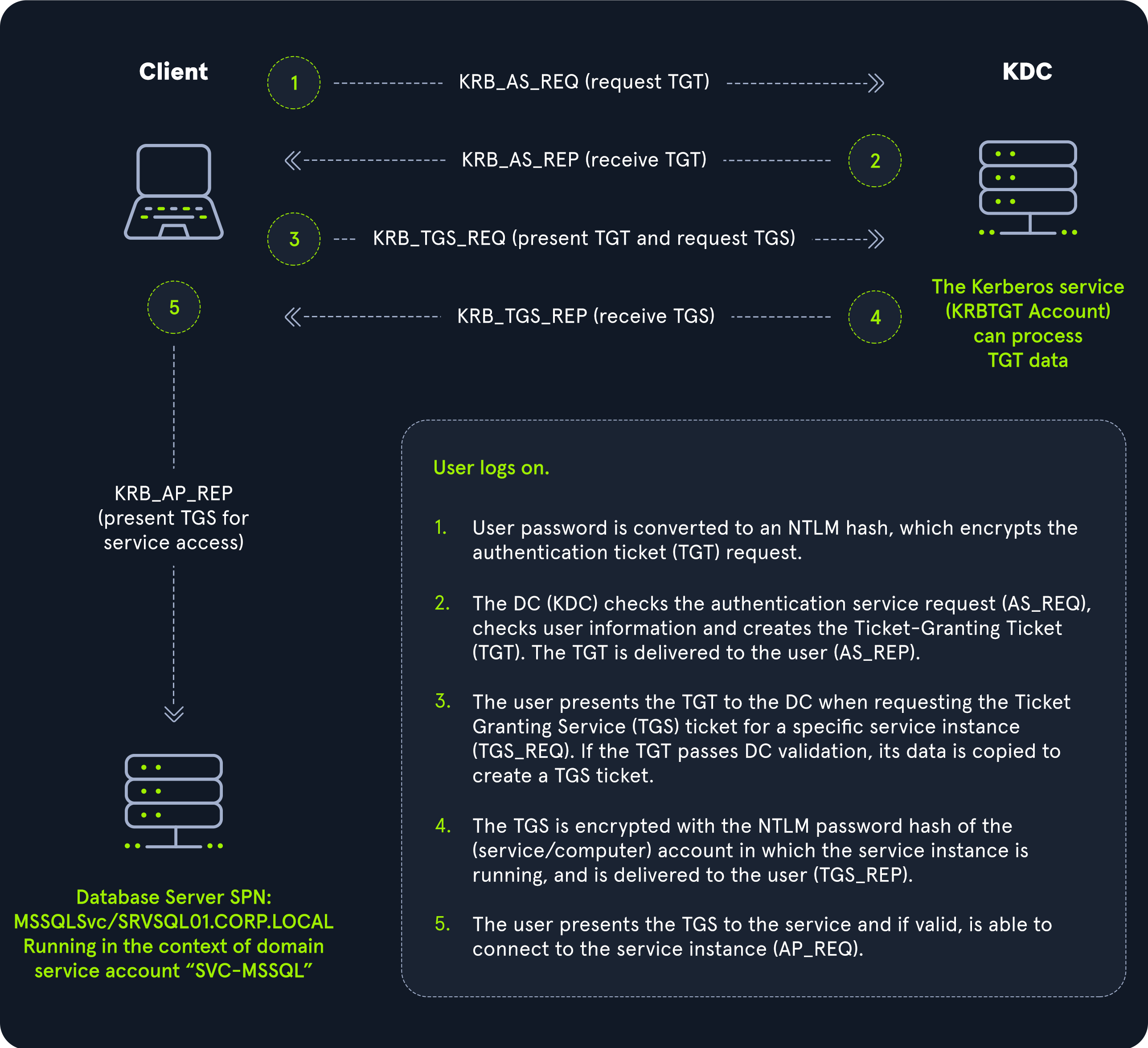
| 1. When a user logs in, their password is used to encrypt a timestamp, which is sent to the Key Distribution Center (KDC) to verify the integrity of the authentication by decrypting it. The KDC then issues a Ticket-Granting Ticket (TGT), encrypting it with the secret key of the krbtgt account. This TGT is used to request service tickets for accessing network resources, allowing authentication without repeatedly transmitting the user’s credentials. This process decouples the user’s credentials from requests to resources. |
| 2. The KDC service on the DC checks the authentication service request (AS-REQ), verifies the user information, and creates a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT), which is delivered to the user. |
| 3. The user presents the TGT to the DC, requesting a Ticket Granting Service (TGS) ticket for a specific service. This is the TGS-REQ. If the TGT is successfully validated, its data is copied to create a TGS ticket. |
| 4. The TGS is encrypted with the NTLM password hash of the service or computer account in whose context the service instance is running and is delivered to the user in the TGS_REP. |
| 5. The user presents the TGS to the service, and if it is valid, the user is permitted to connect to the resource (AP_REQ). |
Kerberos Authentication Process
| 1. When a user logs in, their password is used to encrypt a timestamp, which is sent to the Key Distribution Center (KDC) to verify the integrity of the authentication by decrypting it. The KDC then issues a Ticket-Granting Ticket (TGT), encrypting it with the secret key of the krbtgt account. This TGT is used to request service tickets for accessing network resources, allowing authentication without repeatedly transmitting the user’s credentials. This process decouples the user’s credentials from requests to resources. |
| 2. The KDC service on the DC checks the authentication service request (AS-REQ), verifies the user information, and creates a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT), which is delivered to the user. |
| 3. The user presents the TGT to the DC, requesting a Ticket Granting Service (TGS) ticket for a specific service. This is the TGS-REQ. If the TGT is successfully validated, its data is copied to create a TGS ticket. |
| 4. The TGS is encrypted with the NTLM password hash of the service or computer account in whose context the service instance is running and is delivered to the user in the TGS_REP. |
| 5. The user presents the TGS to the service, and if it is valid, the user is permitted to connect to the resource (AP_REQ). |

The Kerberos protocol uses port 88 (both TCP and UDP). When enumerating an Active Directory environment, we can often locate Domain Controllers by performing port scans looking for open port 88 using a tool such as Nmap.